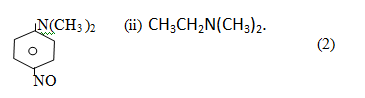Sample Paper of Chemistry 2014 for class 12, CBSE. Paper No.2
SAMPLE PAPER – 2014
CLASS – XII
SUBJECT – Chemistry
General instructions:
1All questions are compulsory.
2Marks for each question are indicated against it.
3Questions number 1to 8 are very short –answer questions, carrying 1 mark each. Answer these in one word or about one sentence each.
4Questions number 9 to18 are short –answer questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer these in about 30 words each.
5Questions number19 to27 are short –answer questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer these in about 40 words each.
6Questions number28 to30 are long-answer questions of 5 marks each. Answer these in about 70 words each.
7 Use log tables, if necessary. Use of calculators is not permitted
CHEMISTRY BLUE PRINT CLASS XII
| S.NO | CHAPTER | S.A(1) | S.A(2) | S.A(3) | L.A(5) | TOTAL |
| 1 | HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES | NIL | 1X(2) | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 2 | ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS | NIL | 1X(2) | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 3 | ALDEHYDES, KETONES… | NIL | NIL | NIL | 1X(5) | 5 |
| 4 | AMINES | 1X(1) | 2X(2) | NIL | NIL | 5 |
| 5 | COORDINATION COMPOUNDS | NIL | 1X(2) | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 6 | SURFACE CHEMISTRY | NIL | 1X(2) | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 7 | ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS | 2X(1) | NIL | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 8 | POLYMERS | 2X(1) | NIL | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 9 | BIOMOLECULES | NIL | NIL | NIL | 1X(5) | 5 |
| 10 | SOLUTIONS | 1X(1) | 2X(2) | NIL | NIL | 5 |
| 11 | ELECTROCHEMISTRY | NIL | NIL | NIL | 1X(5) | 5 |
| 12 | CHEMICAL KINETICS | NIL | 1X(2) | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 13 | SOLID STATE | NIL | 1X(2) | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 14 | CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE | 2X(1) | NIL | 1X(3) | NIL | 5 |
| 8 | 20 | 27 | 15 | 70 |
1.Write Hofmann-Bromamide reaction.(1)
2.What are depressants? Give example.(1)
3.Name the process used for refining of (i) Nickel.(1)
- Define addition polymers with two examples . (1)
- Write the structure of monomer of BunaN.(1)
- People living at high altitude generally suffer from anoxia , Explain.(1)
- How is the drug Cimetidine found to be more effective in controlling acidity?(1)
- Which type of drugs form essential component of sleeping pills?(1)
- C4H8Cl2 (A) on hydrolysis forms C4H8O (B) which forms an oxime, but does not reduce Fehling solution. B also gives iodoform test. Identify A and B and explain reactions.(2)
- Ortho and para nitro phenols are more acidic than phenols whereas cresols are less acidic than phenols.Explain why? (2)
Give reasons:
- Why are amines basic in nature?
- Ethylamine is more basic than aniline. (1+1)
12 Give IUPAC name of the following.
13 A group 14 element is to be converted into n –type semi conductor by doping it with suitable impurity .To which group should this impurity belong? What is this type of defect called? (2)
14 (a) Write linkage isomer of [Co (NH3)5 NO2 ] Cl 2
(b)Explain the splitting of d-orbital in a octahedral complex? (2)
15 In a process adsorbate and adsorbent are held by strong force like a chemical bond. Name the type of adsorption? Write other two characteristics of such type of adsorption. (2)
16State Raoult’s law for solution containing Volatile and non-volatile solute.(2)
17 i) Out of 1M solution of Sugar and 1 M solution of Urea, which will have greater boiling point? Why.
(ii)What is reverse osmosis? Give its application.(2)
- A greater insight in to the energetic and mechanistic aspects of reactions”. Explain the above statement which was given by “Max Trautz” and William Lewis” (2)
- (i) C4H8Cl2 (A) on hydrolysis forms C4H8O (B) which forms an oxime, but does not reduce Fehling solution. B also gives iodoform test. Identify A and B and explain reactions.
(ii)Convert benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol.(2+1)
- Carry out the following conversions:
- Ethanol to 2 propanol
- Acetaldehyde in to 2- butenol
- Acetone to 2 butyl alcohol (3)
21 Write IUPAC names of the following:
- K3 [Fe (C2O4)3]
- [PtCl (NH3)5] Cl3.
- [Pt Cl (NH2CH3) (NH3)2] Cl. (3)
22 Account for the following:
(i)Fe(OH)3 sol is positively charged
(ii) The extent of physical adsorption decreases with rise in temperature
(iii) A delta is formed at appoint where river enters the sea. (3)
23 Following method of extracting Zn is based on thermodynamics:
(a) 2ZnS + 3O2 2ZnO + 2SO2
(b) ZnO +C Zn + CO
ΔG0f( in kJ mol-1) for ZnS=-205.4 ZnO=-318.2 SO2=-300.4 CO=-137.3
Calculate free energy changes of the above reactions and comment on the result. (3)
24 Explain mechanism of free radical polymerization. (3)
25 On heating, arsine(AsH3) decomposes as: 2AsH3(g)®2As(s) +3H2
The total pressure measured at constant temperature and constant volume varies with time as follows: Calculate the rate constant assuming the reaction to follow the first order rate law. (3)
| t(min) | 0 | 5 | 7.5 | 10 |
| p/mmHg | 760 | 836 | 866.4 | 896.8 |
26 The unit cell of aluminium is a cube with an edge length of 405pm. The density of aluminium is 2.70 g/cm3. What type of unit cell of aluminium is? (3)
27(i) What are artificial sweetening agents?
(ii) Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
(iii) What problem arises in using alitame as artificial sweetener? (3)
28 An organic compound (A) having molecular formula C9H10O forms an orange red precipitate (B) with , 2,4-DNP reagent. Compound (A) gives a yellow precipitate (C) when heated in the presence of iodine and NaOH along with a colourless compound (D). (A) does not reduce Tollen’s reagent or Fehling’s solution nor does it decolourises bromine water. On drastic oxidation of (A) with chromic acid, a carboxylic acid (E) of molecular formula (C7H6O2) is formed. Deduce the structures of the organic compounds (A) to (E). (5)
OR
Give reasons:
- Ethanal is more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions than propanone.
- HCHO reacts with HCN faster than CH3
- Acetaldehyde gives aldol condensation while formaldehyde does not.
- Ethanoic acid is highly soluble in water but hexanoic acid is only slightly soluble.
- A carboxylic acid does not form an oxime although there is present a carbonyl group in carboxylic functional group. (5)
29 Answer the following questions briefly:
(i) What are any two good sources of vitamin A?
(ii) What are nucleotides?
(iii) What are enzymes?.
(b) How are carbohydrates classified? (3+2)
OR
(a)State differences between the following:
(i) a- helix and b pleated sheet structure.
(ii) Primary and secondary structure of a protein.
(iii) Enzymes and co-enzymes.
(b) What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each.
30 (a) With the help of a graph , explain why it is not easy to determine l0 for a weak electrolyte by extrapolating the concentration versus molar conductivity curve as for strong electrolytes. (2)
(b) For the cell , Mg½Mg2+(aq) ½½Ag+(aq)½Ag, calculate the equilibrium constant at 250C and also the maximum work that can be obtained by operating the cell. E0(Mg½Mg2+)=-2.37V and E0(Ag+½Ag)=+0.80 V (3)
OR
What are primary and secondary cells? Discuss construction and working of lead storage battery. (5)