Download Previous Year Question Paper with Answers of “Financial Market Management – Code 805” for Class 12 NSQF Vocational, CBSE Session 2021-2022.
CBSE | NSQF-Vocational Education
Financial Market Management (Subject Code 805)
Class XII (Session 2021-2022)
Sample Question Paper for Term – II
SECTION A
(3 + 2 = 5 marks)
Answer any 03 questions out of the given 04 questions 1 x 3 = 3
Q.1 Whose are called Service entrepreneurs? 1
Q.2 What do you mean interpersonal Skills? 1
Q.3 What are the sectors of green jobs? 1
Q.4 Define Eco–Tourism. 1
Answer any 01 question out of the given 02 questions 1 x 2 = 2
Q.5 Describe Startups for the new Entrepreneurs. 2
Q.6 Write the benefits of green jobs. 2
SECTION B
(5 + 6 + 6 = 17 marks)
Answer any 05 questions out of the given 07 questions 1 x 5 = 5
Q.7 Name the process of delivering securities to the clearing corporation to effect settlement of a sale transaction? 1
Q.8 What is Novation? 1
Q.9 At what price Valuation debit take place? 1
Q.10 Who is called Writer of the option contract? 1
Q.11 What do you mean by European option contract? 1
Q.12 Which contract price is generally not available in public domain? 1
Q.13 Define Initial Margin for Future contract. 1
Answer any 03 questions out of the given 05 questions 2 x 3 = 6
Q.14 Who are called Registered owner and beneficiary owner under The Depositary Act, 1996? 2
Q.15 Describe Standard Form of Contract under the Indian Contract Act 1872. 2
Q.16 Write the Economic Significance of Index Movements. 2
Q.17 What is Impact cost? Write its formula. 2
Q.18 Describe Pricing of Future. 2
Answer any 02 questions out of the given 04 questions 3 x 2 = 6
Q.19 Write the Price sensitive information under SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015? 3
Q.20 Describe International Securities Identification Number. 3
Q.21 What is index Derivatives contract? Write its advantages. 3
Q.22 Define In- the-Money, At-the-Money and Out-of-the-Money Option Contracts. 3
SECTION C (2 x 4 = 8 marks)
(COMPETENCY-BASED QUESTIONS)
Answer any 02 questions out of the given 03 questions
Q.23 Several entities involved in the process of clearing and settling the trades executed on Exchanges. Write the role of each agency. 4
Q.24 Index reflects the whole market. Explain various computational methodologies to construct the indices. 4
Q.25 Future contract in the derivative market measure the final position at the expiry. Describe the Payoff position of Buyer and Seller of the Future contract. Explain Diagrammatically. 4
ANSWERS
SECTION A (3 + 2 = 5 marks)
Answer any 03 questions out of the given 04 questions 1 x 3 = 3
1.
Answer: These entrepreneurs either create a new market for their services or provide a service in an existing market. (1)
2.
Answer: it means the competencies required to work with other people. (1)
3.
Answer: These are mainly energy, material, water conservation, waste management and pollution control. (1)
4.
Answer: it experience to visitors to understand the importance of conserving resources, reducing waste, enhancing the natural environment and reducing pollution. (1)
Answer any 01 question out of the given 02 questions 1 x 2 = 2
5.
Answer:
1. A startup is a company that is in the first stage of its operations. (1)
2. A startup and a traditional business venture are different, most notably for the way they think about growth.(1)
6.
Answer:
increase the efficiency of energy and raw material. (1/2)
reduce greenhouse gas emissions.(1/2)
control waste and pollution.(1/2)
protect and restore ecosystems(1/2)
SECTION B
(5 + 6 + 6 = 17 marks)
Answer any 05 questions out of the given 07 questions 1 x 5 = 5
7.
Answer: Pay-in of Securities 1
8.
Answer: NSCCL becomes the legal counterparty to the net settlement obligations of every member. This principle is called ‘novation’. 1
9.
Answer: The closing price on the day previous to the day of valuation. 1
10.
Answer: Seller of the Option Contract 1
11.
Answer: An option can be exercised at the expiry of the contract period. 1
12.
Answer: Forward Contract 1
13.
Answer: The amount that must be deposited in the margin account at the time a futures contract is first entered into is known as initial margin. 1
Answer any 03 questions out of the given 05 questions 2 x 3 = 6
14.
Answer:
Registered Owner is Depositary (1)
Beneficiary Owner is Demat Account holder (1)
15.
Answer:
A standard form contract is a pre-established record of legal terms regularly used by a business entity or firm in transactions with customers.(1)
A Standard Form Contract is effective upon acceptance.(1)
16.
Answer:
1. News about the company- micro economic factors (e.g. a product launch, or the closure of a factory, other factors specific to a company).(1)
2. News about the economy – macro economic factors (e.g. budget announcements, changes in tax structure and rates, political news such as change of national government, other factors common to all companies in a country). (1)
17.
Answer: Impact cost represents the cost of executing a transaction in a given stock, for a specific predefined order size, at any given point of time. It Measures the Liquidity. (1)
Formula: Impact Cost = 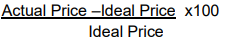
18.
Answer: The cost of carry model used for pricing futures. The Cost of carry is the cost incurred when you hold a certain investment position.
This includes interest costs, margin expenses, financial expenses for advisors, fees, etc. (1)
F = Se^rt (1)
where:
r = Cost of financing (using continuously compounded interest rate)
T = Time till expiration in years
e =2.71828
Answer any 02 questions out of the given 04 questions 3 x 2 = 6
19.
Answer: Price sensitive information means any information which is related directly or indirectly to a company and which if published is likely to materially affect the price of securities of a company.(1)
(a) periodical financial results of the company.(1)
(b) intended declaration of dividends (both interim and final).(1)
20.
Answer: Numbering System of ISIN: The numbering structure for securities in NSDL is of 12 digit alpha numeric string. The first two characters represent country code i.e. IN (in accordance with ISO 3166). (1)
The third character represents the Issuer Type. The list may be expanded as per need. Maximum issuer types can be 35 (A to Z and 0 to 8. The partly paid up shares are identified by 9). The next 4 characters (fourth to seventh character) represent company identity of which first 3 characters are numeric and fourth character is alpha character. (1)
The next two characters (the eighth and ninth characters) represent security type for a given issuer. Both the characters are numeric. The next two characters (the tenth and eleventh characters) are serially issued for each security of the issuer entering the system. Last digit is check digit. (1)
21.
Answer: Index derivatives are derivative contracts which have the index as the underlying. The most popular index derivative contracts the world over are index futures and index options.(1)
Index derivatives offer ease of use for hedging any portfolio irrespective of its composition.(1)
Stock index, being an average, is much less volatile than individual stock prices. This implies much lower capital adequacy and margin requirements.(1)
22.
Answer:
An in-the-money (ITM) option would lead to a positive cash flow to the holder if it were exercised immediately. A call option on the index is said to be in the-money when the current index stands at a level higher than the strike price (i.e. spot price > strike price). (1)
An at-the-money (ATM) option would lead to zero cash flow if it were exercised immediately. An option on the index is at-the-money when the current index equals the strike price (i.e. spot price = strike price). (1)
An out-of-the-money (OTM) option would lead to a negative cash flow if it were exercised immediately. A call option on the index is out-of-themoney when the current index stands at a level which is less than the strike price (i.e. spot price < strike price). (1)
SECTION C
(2 x 4 = 8 marks)
(COMPETENCY-BASED QUESTIONS)
Answer any 02 questions out of the given 03 questions
23. Answer
Several entities involved in the process of clearing and settling the trades executed on Exchanges. Write the role of each agency. (1×4)
Clearing Corporation (NSCCL): The NSCCL is responsible for post-trade activities of a stock exchange. Clearing and settlement of trades and risk management are its central functions. (1)
Clearing Members: They are responsible for settling their obligations as determined by the NSCCL. They have to make available funds and/or securities in the designated accounts with clearing bank/depository participant, as the case may be, to meet their obligations on the settlement day. (1)
Custodians: A custodian is an entity who is responsible for safeguarding the documentary evidence of the title to property like share certificates, etc. In NSCCL, custodian is a clearing member but not a trading member. (1)
Clearing Banks: Clearing banks are a key link between the clearing members and NSCCL for funds settlement. Every clearing member is required to open a dedicated settlement account with one of the clearing banks. Based on his obligation as determined through clearing, the clearing member makes funds available in the clearing account for the pay-in and receives funds in case of a pay-out.(1)
24.
Answer:
A good index is a trade-off between diversification and liquidity.
The computational methodology followed for construction of stock market indices are
Free Float Market Capitalization Weighted Index,
Market Capitalization Weighted index and the
Price Weighted Index. (1)
Free Float Market Capitalisation Weighted index: The free float factor (Investible Weight Factor), for each company in the index is determined based on the public shareholding of the companies as disclosed in the shareholding pattern submitted to the stock exchange by these companies
The Free float market capitalization is calculated in the following manner:
Free Float Market Capitalisation = Issue Size * Price * Investible Weight
Factor The Index in this case is calculated as per the formulae given below: (1)
![]()
Market Capitalisation Weighted index: In this type of index calculation, each stock in the index affects the index value in proportion to the market value of all shares outstanding. In this the index would be calculated as per the formulae below: (1)
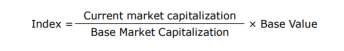
Price Weighted index: In a price weighted index each stock influences the index in proportion to its price per share. The value of the index is generated by adding the prices of each of the stocks in the index and dividing then by the total number of stocks. (1)
25.
Answer:
Payoff means the returns from either buying or selling a futures contract as against buying or selling the underlying asset. Payoff is positive if the position held brings profits to the holder, the payoff is negative if the position held brings losses to the holder. Futures contracts have linear or symmetrical payoffs.(1)
Payoff for buyer of futures: Long futures

The above shows the profits/losses for a long futures position. The investor bought futures when the index was at 6000. If the index goes up, his futures position starts making profit. If the index falls, his futures position starts showing losses. (1 ½)
Payoff for seller of futures: Short futures

The shows the profits/losses for a short futures position. The investor sold futures when the index was at 6000. If the index goes down, his futures position starts making profit. If the index rises, his futures position starts showing losses. (1 ½)






















