Learn Fundamentals of Java Programming “User Defined Methods in Java Programming ” Lesson 23
Data Input
The programs we have written up to now haven’t been interactive. A program is interactive if it is able to take input from the user and respond accordingly. Let us write a program to take user input. To take user input we use the prebuilt Scanner class. This class is available in the java.util package. First we import this class,
import java.util.Scanner;
Now we create an object of the class Scanner. The constructor of this class requires the source from which input is to be taken. Since we will take input from the console, we use the System.in object.
Scanner user_input = new Scanner(System.in );
Then, we invoke the next() method of the Scanner class that returns the token read from the input stream as a String object.
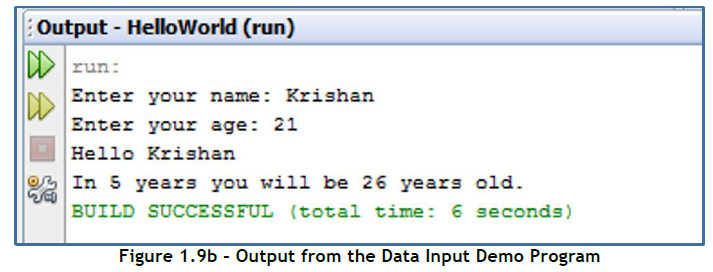
String name = user_input. next( );
System.out.println(“Hello “+ name);
To read numeric data input, again a Java prebuilt class comes to our rescue. This time we use the Integer class. The class has a static method parseInt() that takes a String as parameter and returns the equivalent integer.
String age_string = user_input.next( );
int age = Integ er.parseInt (age_string);
System.out.print(“In 5 years you will be “+ (age +5));
System.out.println(” years old.”);
Since the Integer class is in the java.lang package, which is already imported for all classes, we do not need to import the package. Similarly to the Integer class, there is the Float class with a parseFloat() method, a Double class with a parseDouble() method, and other such classes, that you can use to read Strings and convert them to the required data type.
Figure 1.9a – Data Input Demo Program