Plants and minerals, Class 9 & 10 Science Project
Plants and minerals
Buy some mineral plant food and make up a solution following the directions on the package. Grow two radish plants in clean sand in different containers. Give one water with minerals. Give the other only water. In a few weeks the one without minerals looks sickly and weak. In a few more weeks it may die.
You already know that a plant needs water and carbon dioxide to make sugar, which it uses for food. Part of this sugar is changed into the body of the plant to make it grow. In addition to sugar, the body of the plant needs certain minerals. The most important are: nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus, calcium, potassium and magnesium.
Water dissolves minerals in the ground and carries them up through the roots and stem to all parts of the plant.
When you burn wood and other plant materials, the ashes that are left are the minerals that were taken in by the water coming up from the ground.
Holes in the Leaves
Try this experiment. Gently rub petroleum jelly (such as Vaseline) on the under sides of the leaves of a young plant. Do the same with the tops of the leaves of another plant of the same kind. Give both of them water, minerals and sunlight.
The plant with the petroleum jelly rubbed on the undersides of its leaves dies. The other one lives. Why? There are little openings on the under sides of leaves. Carbon dioxide from the air gets into the plant through these tiny holes. If you plug up these openings you stop carbon dioxide from getting in and the plant can’t make food. Then it can’t live long.
The petroleum jelly on the tops of the leaves doesn’t affect the plant because no openings are blocked.
The holes on the under sides of leaves have another purpose. Water travels up the stem from the roots and goes out of the plant through the leaves. If water cannot get out through the holes in the leaves, new water with minerals doesn’t come in.
You can see water go up the stem to the leaves of a plant by trying this experiment. Cut off an inch of the bottom of a celery stalk with leaves. Put the cut celery into water colored with ink. In about an hour the leaves and stem are streaked with color.
Cut off another small piece from the bottom. Notice the colored spots along the cut end. These are the ends of little tubes through which the water rises in the stalk. Cut the stalk lengthwise and follow the tubes up to the top.
The Importance of Plants
Try this experiment. Put a goldfish into a small fishbowl. In a day or two you will find it coming up for air at the surface of the water. If you leave it alone it will die because of lack of air! Do not let this happen: Add fresh water when you observe the fish coming to surface for air
It may seem strange to say that there is air in water. But you can see this leaving a glass of cold water on the table. Bubbles of air soon form on the glass as it warms up. These bubbles come from the water.
When a fish uses up the air sup- ply in the water of a small bowl, it must come up to the surface for more air. But this harms the fish and it soon dies.
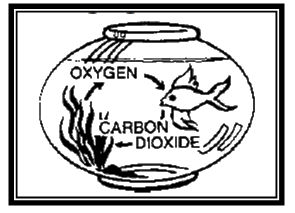
Put the same goldfish into a bowl of water with some water plants. Now the fish lives much longer. While the plant makes food from carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight, it also forms oxygen, most of which it does not need. The fish uses this oxygen to “breathe”.
Do fish help water plants?
When a fish burns up food and oxygen it produces carbon dioxide. This goes back into the water. The water plants then use this carbon dioxide to make more food.So you see that water plants and fish help each other, giving what the other needs.
At home the goldfish gets its food from you. But in nature, in a pond or lake,plants are the basic food supply for fish.
The same thing is true of plants and animal son land. Plants not only supply food for animals, they also form the oxygen in the air. And animals use up some of this oxygen to burn up plant food and make car- bon dioxide to help new plants grow.
But man makes use of plants in other ways. We use them for making cotton cloth, rope, lumber and paper.
Long ago plants captured sun- light and grew to great size. Today we dig up their remains as coal, oil and gas and use them for fuel and to drive cars, trains, ships and airplanes. When we do we are making use of the energy that plants captured from the sun long ago.
We also use plant materials found in coal, oil, wood and gas to make plastics, chemicals and drugs.
So you see that without plants. Civilization would be impossible. In fact we could not remain alive.
Future Food Factories
Scientists are hard at work trying to learn the important secret of the way in which the leaf of a plant makes food from carbon dioxide, Water and sunlight. They would like to be able to do this too.
Perhaps our food could then be made in factories instead of farms. Food might then become cheaper and more plentiful. But so far they have not succeeded. This task remains one of the great challenges for the future. Perhaps you, as a scientist, will someday make an important discovery about plants that will help make this dream of mankind come true.
Tips:—
Grow plants under artificial light. A desk lamp may be used. results will be obtained with fluorescent lights. Don’t let the leaves get closer than about 4 inches from the light. In a week or so, depending upon the size of the containers, the one that gets no water shrivels up and begins to die.
Soak a bean for a day to soften it. Pry apart the two halves of the seed and find the tiny leaves, stem and root of the young plant.
Grow a sweet potato vine Place the narrow end in water in a jar or glass. Put it in a dark place until roots and stem start Then put it into the light
Place a quarter over the spot where you plant a bean seed in a pot. Watch how the young plant lifts the coin and pushes it aside.
A drop of iodine on moistened starch makes it turn black. Test beans, potatoes, bread and other food, with iodine after wetting the food. Which foods have starch?
Grow 10 plants in one very small pot and 1 in another. The 10 plants crowd each other and do not grow as tall as the one that is alone in the pot.
Grow a morning glory plant. Watch how the tip of the stem moves in a circle every few hours. Tie a string to an overhead support and watch the plant wind itself around the string.
Cover a young radish plant with a paper cup that has a hole cut out of the back. Watch the plant seek the light by growing out of the hole.
TRY THESE EXPERIMENTS
1. Plant a carrot. Put the narrow end in water in a jar and watch it grow. Do the same with beets, turnips and parsley.
2. Grow potatoes by cutting off a piece with several buds on It and planting it 3inches down in a flower pot.
3. Plant lentils, beans, peas and similar seeds that you can get around the kitchen.
4. Grow an onion by setting the bottom in water in a glass.
5. Grow orange and grapefruit seeds in a flower pot.
6. Grow grass seed on a sponge placed in water in a dish.
7. Does a plant need some darkness? Grow a plant under a fluorescent lamp 24 hours a day. It may not grow as well as one that has a regular period of darkness in every 24 hours.
8. Put some minerals plant food solution in a glass. Place it in the sunlight. Algae, a tiny green plant starts to grow after a while. Pour half of the greenish water into a glass and keep it in the dark. Notice how the one in sunlight becomes much greener.
9. Cut off the leaves of a young plant. See if it grows new leaves.
10. Plant some seeds in a small pot and put it in the refrigerator. Do you think seeds will
develop?
11. Try growing pussy willow, begonia, geranium and ivy from cut stems placed in
moist sand in a flower pot.
12. Directions for radish seeds call for planting at a depth of % inch. Plant some seeds
2 inches deep and see if they come up.
13. Grow a bean plant in darkness and another in bright light. At the beginning the one in
darkness grows much taller, in an attempt to find light. After a while, failing to get
any it dies.
14. Try to grow a plant on a hot radiator. Does the heat harm the plant?
15. Grow a sweet pea plant. Note the long feelers (tendrils) at the tips of the stems. Rub the under side of a tendril and watch it curl up in a few minutes. The purpose of the tendril is to find support for the plant to climb. 16. Give a growing plant mineral solution that is 5 times as strong as called for in the directions on the package. See how this affects the plant.
17. Plant stores sell a growth material called “gibberellin’. Apply it to several plants according to directions on the package and compare the increase in growth with plants grown in the regular way.